# 一、准备工作
MyBatis工作流程:应用程序首先加载mybatis-config.xml配置文件,并根据配置文件的内容创建SqlSessionFactory对象;然后,通过SqlSessionFactory对象创建SqlSession对象,SqlSession接口中定义了执行SQL语句所需要的各种方法。之后,通过SqlSession对象执行映射配置文件中定义的SQL语句,完成相应的数据操作。最后通过SqlSession对象提交事务,关闭SqlSession对象,整个过程具体实现如下:就按照下面的流程进行源码分析
public void test01() throws IOException {
// 1、获取sqlSessionFactory对象
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
// 2、获取sqlSession对象
SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
// 3、获取接口的实现类对象
//会为接口自动的创建一个代理对象,代理对象去执行增删改查方法
EmployeeMapper mapper = openSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
Employee employee = mapper.getEmpById(1);
System.out.println(mapper);
System.out.println(employee);
} finally {
openSession.close();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 二、SqlSessionFactory 对象的初始化过程
SqlSessionFactory对象的初始化序列图如下:
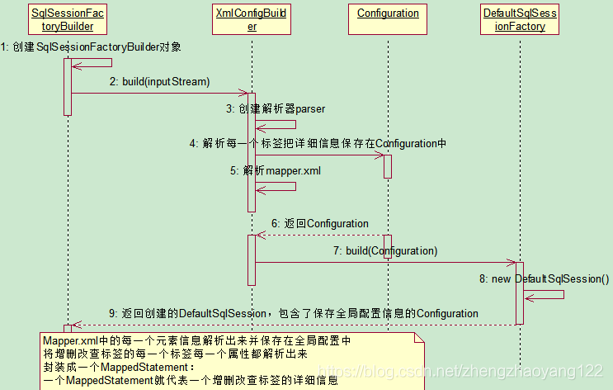
【1】 从这行代码入手,首先创建了一个SqlSessionFactoryBuilder工厂,这是一个建造者模式的设计思想,由builder建造者来创建SqlSessionFactory工厂。
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
【2】 然后调用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder中的build方法传递一个InputStream输入流,Inputstream输入流就是配置文件 mybatis-config.xml,SqlSessionFactoryBuilder根据传入的InputStream输入流和environment、properties属性创建一个 XMLConfigBuilder对象(解析器)。SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象调用XMLConfigBuilder的parse()方法。配置文件中的内容被解析后封装到Configuration对象中。同时解析mapper标签。返回一个XPathParser类型的实例。
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
//创建文件的解析器 XPathParse
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
}
//进入上述的内部方法 parser.parse()
public Configuration parse() {
parsed = true;
//获取 configuration 标签,全局最大的标签
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
//进入上述的内部方法 parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
// 此方法中的方法内部都是将解析的标签内容 set 进 configuration 对象中
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
Properties settings = settingsAsPropertiess(root.evalNode("settings"));
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
//......
//将 setting 标签中的全局变量都set 到configuration 对象中
settingsElement(settings);
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
//解析mapper 标签:很重要
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
}
//列举上述 settingsElement(settings); 内部的源码
private void settingsElement(Properties props) throws Exception {
configuration.setAutoMappingBehavior(AutoMappingBehavior.valueOf(props.getProperty("autoMappingBehavior", "PARTIAL")));
//false 表示默认值
configuration.setUseGeneratedKeys(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("useGeneratedKeys"), false));
configuration.setDefaultExecutorType(ExecutorType.valueOf(props.getProperty("defaultExecutorType", "SIMPLE")));
configuration.setDefaultStatementTimeout(integerValueOf(props.getProperty("defaultStatementTimeout"), null));
//......
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
【3】解析mapper.xml文件,也是通过XPathParser类型的解析器,具体源码如下:将结果保存在Configuration中
/** 配置信息如下:
<mappers>
<mapper resource="EmployeeMapper.xml" />
</mappers>
**/
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
//将配置文件转化为流文件,mapper.xml 文件
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
//解析 mapper.xml 文件
mapperParser.parse();
}
}
}
}
//进入 mapperParser.parse(); 方法
public void parse() {
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
//解析 mapper标签中的内容
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingChacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}
//进入 configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper")); 方法
//解析mapper中的标签内容
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
//解析增删改查标签
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
【4】解析mapper中的增删改查标签:拿到所有标签能写的属性,将详细信息保存进MappedStatement(是一个Map,Key存放的是命令空间+id)中,一个MappedStatement就代表一个增删改查标签的详细信息。
// 进入增删改查标签的源码 buildStatementFromContext
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
for (XNode context : list) {
//获取到 解析增删改查标签的解析器 statementParser
final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context, requiredDatabaseId);
//解析标签中的内容
statementParser.parseStatementNode();
}
}
public void parseStatementNode() {
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
return;
}
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
//....
//将解析的结果进行封装
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
}
}
//进入 builderAssistant.addMappedStatement 方法
public MappedStatement addMappedStatement(
//......
MappedStatement statement = statementBuilder.build();
//并将结果添加到 Configuration 中,MappedStatement 是一个 map 对象
configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);
return statement;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
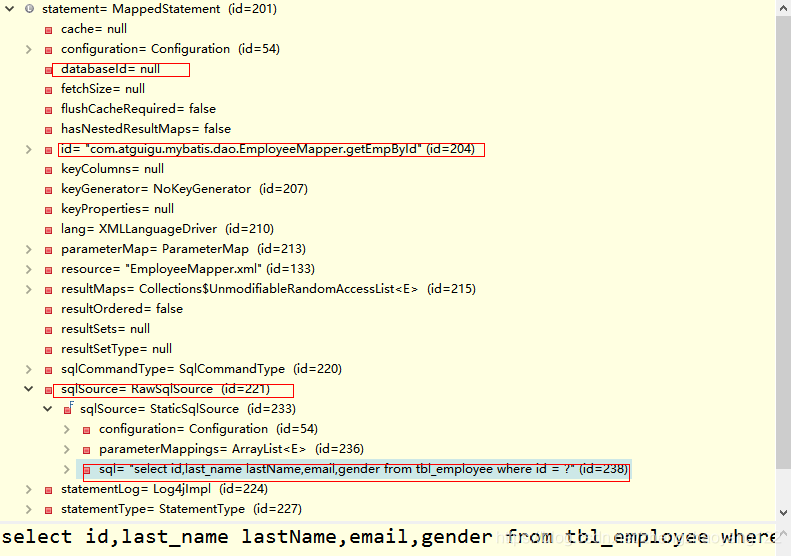
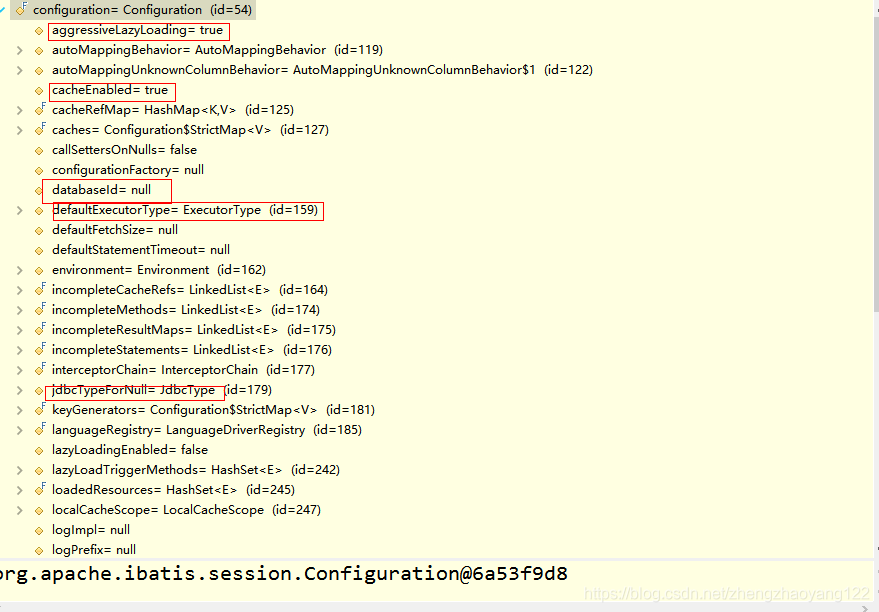
【5】Configuration对象保存了所有配置文件的详细信息,包括全局配置文件和sql映射文件。
Configuration中包含的MappedStatement对象信息:
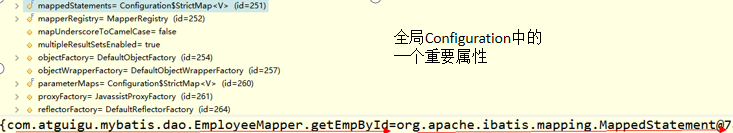
Configuration中包含的MapperRegistory对象,其中的knownMappers包含的是接口的代理对象。

【6】DefaultSqlSessionFactory:传入上面返回的Configuration对象,通过build的方法创建一个DefaultSqlSessionFactory包含配置了全局信息的Configuration;
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
2
3
DefaultSqlSessionFactory : SqlSessionFactory的默认实现类,是真正生产会话的工厂类,这个类的实例的生命周期是全局的,它只会在首次调用时生成一个实例(单例模式),就一直存在直到服务器关闭。
# 三、SqlSession 对象的初始化过程
SqlSession对象的初始化序列图如下:会创建Executor
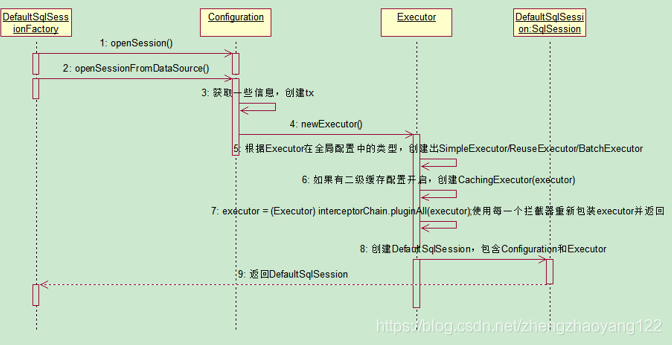
SqlSession对象是MyBatis中最重要的一个对象,这个接口能够让你执行命令,获取映射,管理事务。SqlSession中定义了一系列模版方法,让你能够执行简单的CRUD操作,也可以通过getMapper获取Mapper层,执行自定义SQL语句,因为SqlSession在执行SQL语句之前是需要先开启一个会话,涉及到事务操作,所以还会有commit、rollback、close等方法。这也是模版设计模式的一种应用。
【1】通过DefaultSqlSessionFactory的openSession方法获取SqlSession;
SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
【2】进入openSession方法:需要传入Executor的类型,在配置文件中可以指定,默认是simple;
public SqlSession openSession() {
//configuration.getDefaultExecutorType() 执行器Executor 的默认类型 simple(总共三种类型 reuse、simple、batch)
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
2
3
4
【3】进入openSessionFromDataSource方法:重点是创建了Executor执行器对象和SqlSession对象,传入事务和类型。
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
//创建事务
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
//四大组件之一 Executor
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
【4】进入创建Executor的方法:configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType); Exeutor是用来做增删改查的,里面包含了query等方法;
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
//根据类型创建对应的 Executor
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
//默认的 executor 是 SimpleExecutor
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
//是否开启的二级缓存,好处是查询之前会先从缓存中获取
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
//每一个 executor 都需要通过 拦截器进行重新包括(插件使用。。。。重要)
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
【5】展示Executor对象中的信息:
public interface Executor {
//增删改查操作
int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException;
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey cacheKey, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException;
List<BatchResult> flushStatements() throws SQLException;
//事务相关操作
void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException;
void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException;
//......
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
【6】创建DefaultSqlSession并将上述创建的Executor传入,并包含Configuration;
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
# 四、getMapper 对象的初始化过程
getMapper对象的初始化序列图如下:会创建MapperProxy代理对象;MapperProxy是Mapper映射SQL语句的关键对象,我们写的 Dao层或者Mapper层都是通过MapperProxy来和对应的SQL语句进行绑定的。下面我们就来解释一下绑定过程。
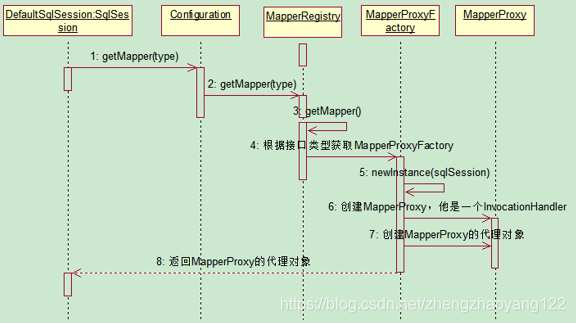
【1】通过getMapper获取代理对象;
EmployeeMapper mapper = openSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
【2】进入getMapper方法内部,发现调用的是Configuration对象的getMapper方法,并将SqlSession作为参数传入;
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return configuration.<T>getMapper(type, this);
}
2
3
【3】进入Configuration对象的getMapper方法,通过调用mapperRegistry对象的getMapper方法;
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
2
3
【4】进入MapperRegistry的getMapper方法,根据接口类型获取其代理对象工厂mapperProxyFactory;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
//根据接口类型获取其代理对象
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
// 会创建一个 mapperProxy
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
【5】进入mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);方法,其主要是创建MapperProxy代理对象;
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
//获取代理对象
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
2
3
4
5
【6】进入MapperProxy代理对象,主要包含如下三个属性:并且实现了InvocationHandler,是JDK动态代理的一部分;
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L;
//主要包含 sqlSession 、 mapper接口和 其中的方法
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache;
//......
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
【7】我们进入5中的newInstance方法:使用JDK实现动态代理Proxy.newProxyInstance(....),创建MapperProxy代理对象。内部包含SqlSession进行增删改查。也就是说,MyBatis中Mapper和SQL语句的绑定正是通过动态代理来完成的。通过动态代理,我们就可以方便的在Dao层或者Mapper层定义接口,实现自定义的增删改查操作了。
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
//JDK 动态代理
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
2
3
4
5
【8】代理对象展示:
# 五、通过代理对象调用目标方法的初始化过程
mapper.getEmpById(1)查询执行的序列图如下:
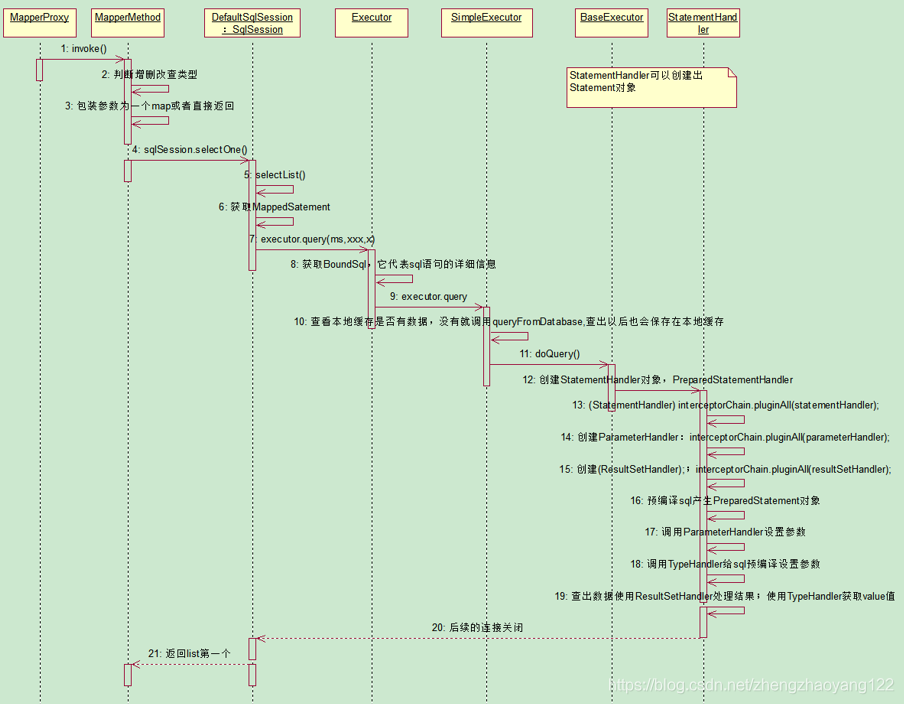
【1】进入代理类调用目标方法入口:
Employee employee = mapper.getEmpById(1);
【2】首先会进入代理方法的invoke方法:
//调用代理对象的入口
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//首先判断调用的是不是 Object 对象的方法
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
try {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
//将当前方法包装成 MapperMethod
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
【3】进入mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);目标方法执行,传入sqlSession和参数;
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
//当前方法无返回值时执行
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
//返回多个执行方法
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
//返回Map执行
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
//返回游标执行
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
//其余执行此方法
//该方法是将当前参数:如果是1个参数则返回,如果多个则组装成 map 返回
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
break;
return result;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
【4】调用单个查询sqlSession.selectOne方法:调用查询多个的方法,返回list的第一个元素即可;statement就是当前sql的唯一表示,对应xml中的namespace;
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
List<T> list = this.<T>selectList(statement, parameter);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
statement="com.ctrip.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapper.getEmpById"(id=117)
hash= 186075799
hash32= 0
value= (id= 40)
2
3
4
【5】进入selectList(statement, parameter);方法:会获取mapperedStatement对象,同时调用Executor的query方法执行
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
//首先获取 mapperedStatement 对象
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
//通过 executor 的query 方法执行
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
【6】获取mapperedStatement通过BoundSql它代表sql语句的详细信息:通过query方法进行查询;
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
2
3
4
5
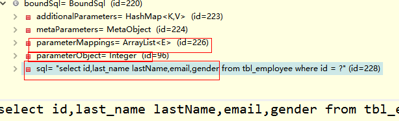
【7】进入上述的query方法,先调用cacheExecutor缓存,如果不存在则调用全局配置Executor,我们这里使用的默认 simpleExecutor方法:先会调用二级缓存,再调用一级缓存;如果不存在则执行queryFromDatabase查出以后也会保存在以及缓存中;
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
//先调用本地缓存
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
//如果缓存中不存在,则调用 queryFromDatabase
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
return list;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
【8】进入queryFromDatabase方法:调用BaseExecutor对象中的doQuery方法ms当前增删改查标签的详细信息
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
//原生 JDBC 的 Statement对象
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
//创建四个对象之一 StatementHandler
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
//从 StatementHandler 中获取 Statement 对象
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
【9】进入SimpleExecutor对象的doQuery方法:底层包含了Statement对象,表示对JDBC的封装,同时创建了四大对象之一 StatementHandler作用:创建Statement对象;在创建StatementHandler的时候构造器里面会同时创建ParameterHandler和 ResultSetHandler。
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
//原生 JDBC 的 Statement对象
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
//创建四个对象之一 StatementHandler
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
//从 StatementHandler 中获取 Statement 对象
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
【10】进入newStatementHandler方法,查看StatementHandler对象的创建;
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
//使用拦截器链包装 StatementHandler
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
2
3
4
5
6
【11】进入RoutingStatementHandler方法:我们可以在查询标签中设置StatementType就根据如下方法创建我们需要的Statement对象;默认使用的是PREPARED(预编译的形式),会创建一个PreparedStatementHandler;
public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
switch (ms.getStatementType()) {
case STATEMENT:
delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case PREPARED:
delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case CALLABLE:
delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
default:
throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType());
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
【12】通过StatementHandler创建Statement对象,进入stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());方法:预编译sql产生的PreparedStatement对象,调用四大对象之一 ParameterHandler进行参数的预编译;也是JDBC原生的对象;
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
//创建一个链接
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
//进行预编译
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
//进行参数预编译
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
【13】进入创建ParameterHandler的方法:newParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);同时也调用了 pluginAll方法,通过拦截器链对ParameterHandler进行封装;
public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
ParameterHandler parameterHandler = mappedStatement.getLang().createParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
//也调用了拦截器链
parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
return parameterHandler;
}
2
3
4
5
6
【14】进入创建ResultSetHandler的方法:configuration.newResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, rowBounds, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql);同时也调用了pluginAll方法,通过拦截器链对ParameterHandler进行封装;也输入四大对象之一;用于处理查询得到的数据;
public ResultSetHandler newResultSetHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, RowBounds rowBounds, ParameterHandler parameterHandler,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler = new DefaultResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql, rowBounds);
//也调用了拦截器链
resultSetHandler = (ResultSetHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(resultSetHandler);
return resultSetHandler;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
【15】最终返回执行的结果和关闭连接,以及查询流程总结:
■ StatementHandler:处理sql语句预编译,设置参数等相关工作;
■ ParameterHandler:设置预编译参数用的;
■ ResultHandler:处理结果集;
■ TypeHandler:在整个过程中,进行数据库类型和 javaBean类型的映射;
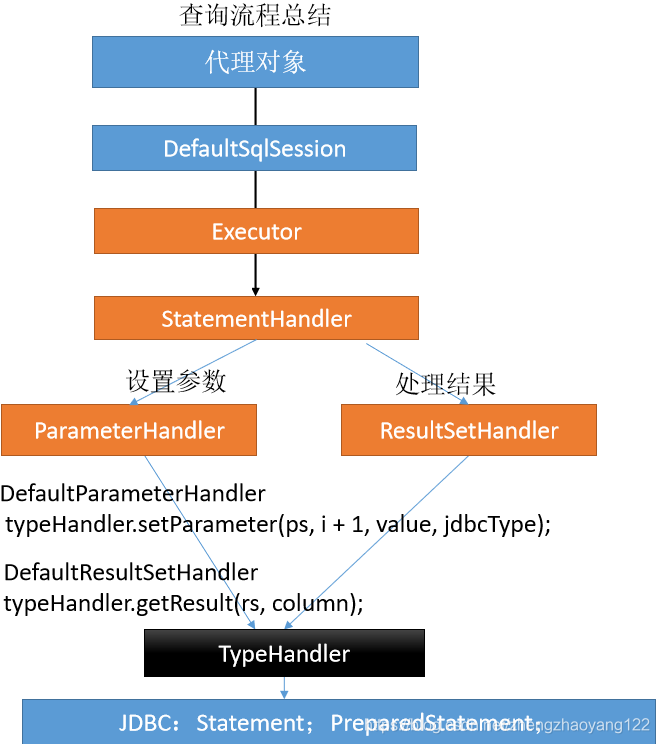
# 六、总结
【1】根据配置文件(全局,sql映射)初始化出Configuration对象;
【2】创建一个DefaultSqlSession对象,他里面包含Configuration以及Executor(根据全局配置文件中的defaultExecutorType创建出对应的Executor);
【3】DefaultSqlSession.getMapper():拿到Mapper接口对应的MapperProxy;
【4】MapperProxy里面有DefaultSqlSession;
【5】执行增删改查方法:
1)、代理对象调用DefaultSqlSession的增删改查(最终调用Executor的增删改查);
2)、会创建一个StatementHandler对象。(同时也会创建出ParameterHandler和ResultSetHandler);
3)、调用StatementHandler预编译参数以及设置参数值,使用ParameterHandler来给sql设置参数;
4)、调用StatementHandler的增删改查方法;
5)、ResultSetHandler封装结果;
注意:四大对象每个创建的时候都有一个interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);后面的插件应用中使用;